Technology
Technologies We Handle
Our technological capabilities and expertise
Electrolyte Manufacturing & Vanadium Recovery Technology
Vanadium Recovery from Unused Resources
We efficiently recover vanadium from electric precipitator ash (EP ash), an industrial waste from petroleum coke (PC) power plants, and extract it in the form of metavanadate (ammonium metavanadate), which is the raw material for electrolyte. We can also recover other valuable materials (NH3, gypsum, etc.) at the same time. Currently, we are developing technology to recover vanadium from other unused resources (e.g., waste catalysts, etc.).

Electric Precipitator Ash (EP ash)

Generated Metavanadate
Electrolyte Manufacturing Technology from Recovered Vanadium
For our electrolyte manufacturing process, we produce tetravalent oxide (V2O4) through a calcination process in a reduction furnace, after going through a metavanadate purification process to remove impurities from the metavanadate raw material. From this tetravalent oxide (V2O4), we further remove impurities and manufacture 3.5-valent electrolyte in an electrolytic reduction tank.

Reduction Furnace
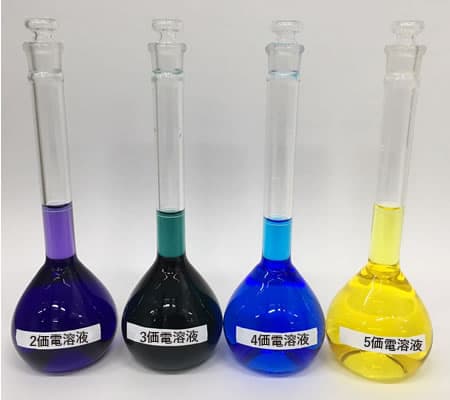

Manufactured Electrolyte
Vanadium electrolyte changes in valence and color depending on the state of charge.
VRFB System Consulting
Vanadium Redox Flow Battery Demonstration
Since our establishment, we have been focusing on the advantages and features of vanadium redox flow batteries and conducting research.
Understanding various performance characteristics of Vanadium Redox Flow Battery (VRFB)
Understanding basic battery components that make up VRFB
Various functional tests and verification required for power storage batteries
Performance evaluation of various electrolytes used in VRFB
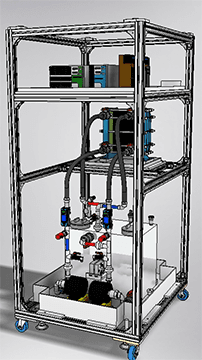
Simple VRFB test device [250W] (manual operation)
Automatic VRFB test device [250W] (automatic operation)
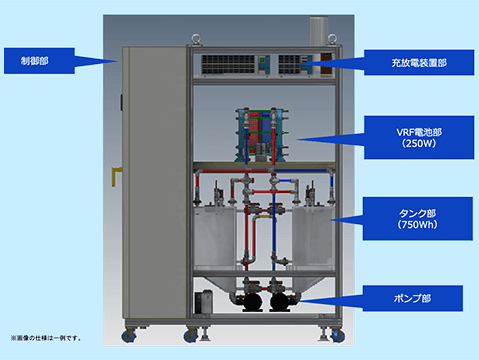
Long-run Test Equipment for Vanadium Electrolyte

Long-run Test Equipment for Vanadium Electrolyte
We have created a redox flow demonstration test device under actual operating conditions and are conducting long-run tests of vanadium electrolyte.
Evaluation Technology
Based on our experience in battery cell manufacturing and battery systems, we have our own system for testing the effects of electrolyte on the battery itself. We conduct performance evaluations using various test equipment as follows.
VRFB Mini-cell Test Equipment
This is a test device for one VRFB cell and is used for various performance evaluations of electrolytes.

Electrolyte Temperature Characteristics Test Equipment
About 10 sets of mini-cell test devices are stored in a thermostatic chamber, allowing for various electrolyte performance evaluations based on temperature characteristics (0°C to 55°C) and limit tests for electrolyte precipitation.

Electrolyte Stability Evaluation Equipment
The electrolyte stability evaluation equipment confirms the stability of the electrolyte, such as precipitation due to temperature. For stability confirmation, we combine a temperature control stage and camera with a microscope to evaluate the stability of positive electrode side vanadium electrolyte (V valence) at high temperatures and negative electrode side vanadium electrolyte (II valence) at low temperatures. (Stability evaluation detects the precipitation state of precipitated particles by changes in the intensity of specific wavelengths, etc.)

Electrolyte Long-run Test Equipment
We repeatedly charge and discharge electrolyte to evaluate its performance. If the electrolyte performance stabilizes after more than 300 cycles of charging and discharging, it can be judged as a stable electrolyte.

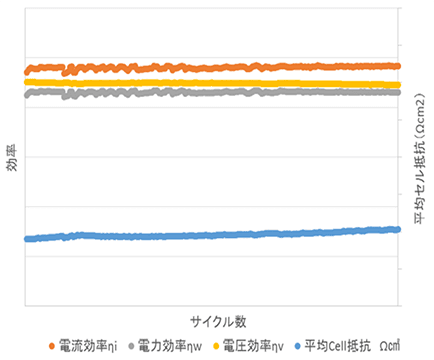
Various Performance Tests Based on Charge-Discharge Cycle Count (Sample)
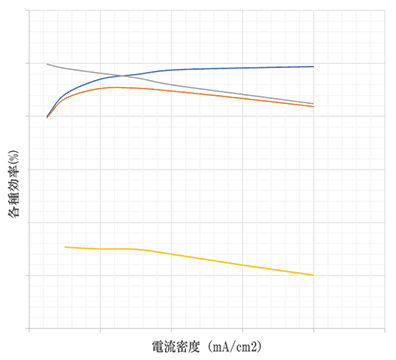
Various Efficiency Tests Depending on Current Density (Sample)