Storage Battery
Introduction to Vanadium Redox Flow Battery technology and products
1. Mechanism of Vanadium Redox Flow Battery (VRFB)
VRFB / Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
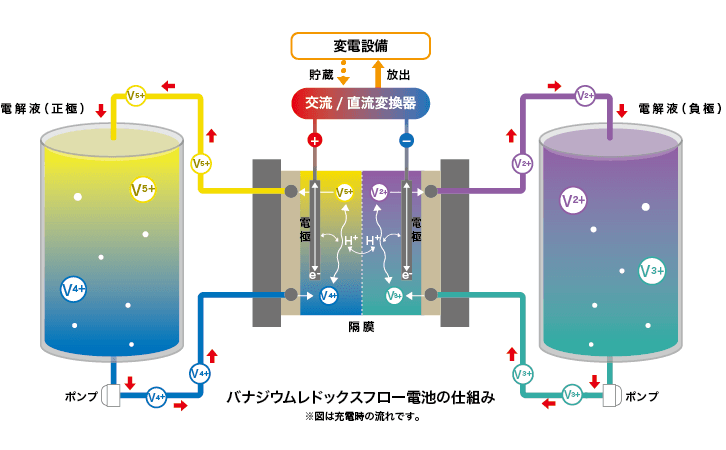
VRFB operates by circulating liquids with different electrode potentials, enabling electron transfer for charging and discharging. Unlike other batteries that charge/discharge through electrode chemical changes, VRFB uses electrolyte chemical changes (redox), allowing it to maintain performance over long periods.
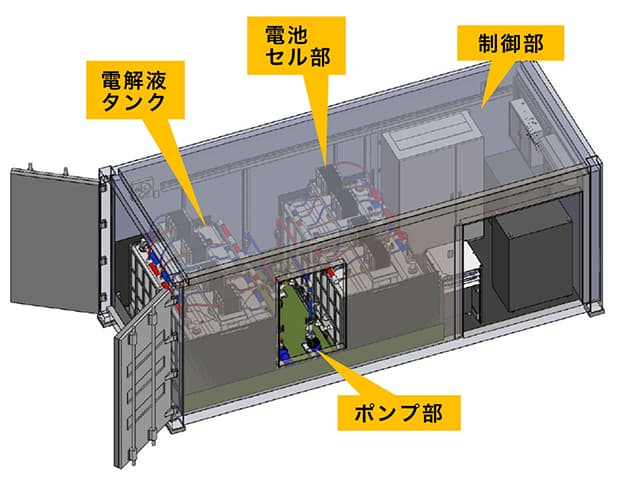
Main Components of VRFB
Battery Cell (Power Unit)
Output unit that charges/discharges through redox reactions of the electrolyte
Electrolyte Tank (Capacity Unit)
Storage unit for the electrolyte
Pump Unit
Pumps electrolyte to the cell unit
Control Unit
Controls cell charging/discharging and electrolyte flow
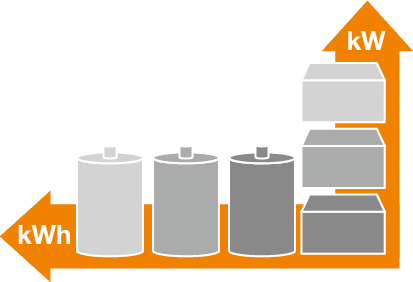
This architecture enables high flexibility to design output (kW) and capacity (kWh) independently.
Vanadium Redox Flow Battery Features
VRFB / Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
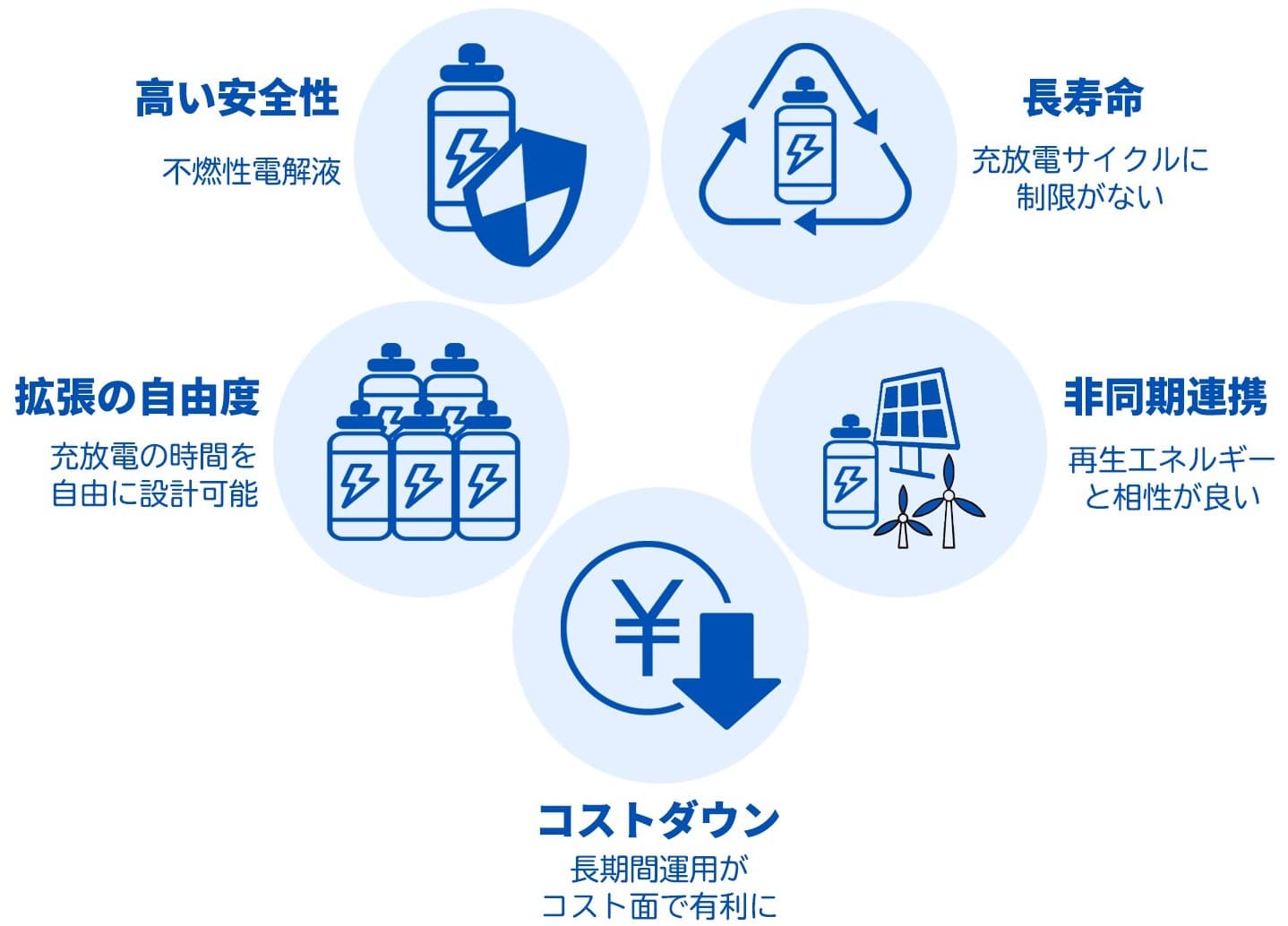
VRFB Features Overview
With unlimited charge and discharge cycles and no degradation, VRFB enables long-term stable operation with high safety and excellent compatibility with renewable energy. VRFB has optimal characteristics as a large-capacity stationary battery for wind and solar power generation that require high safety and stable supply.
Long-term Stable Operation
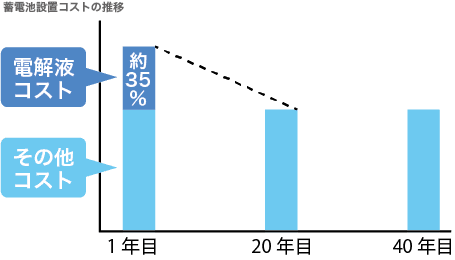
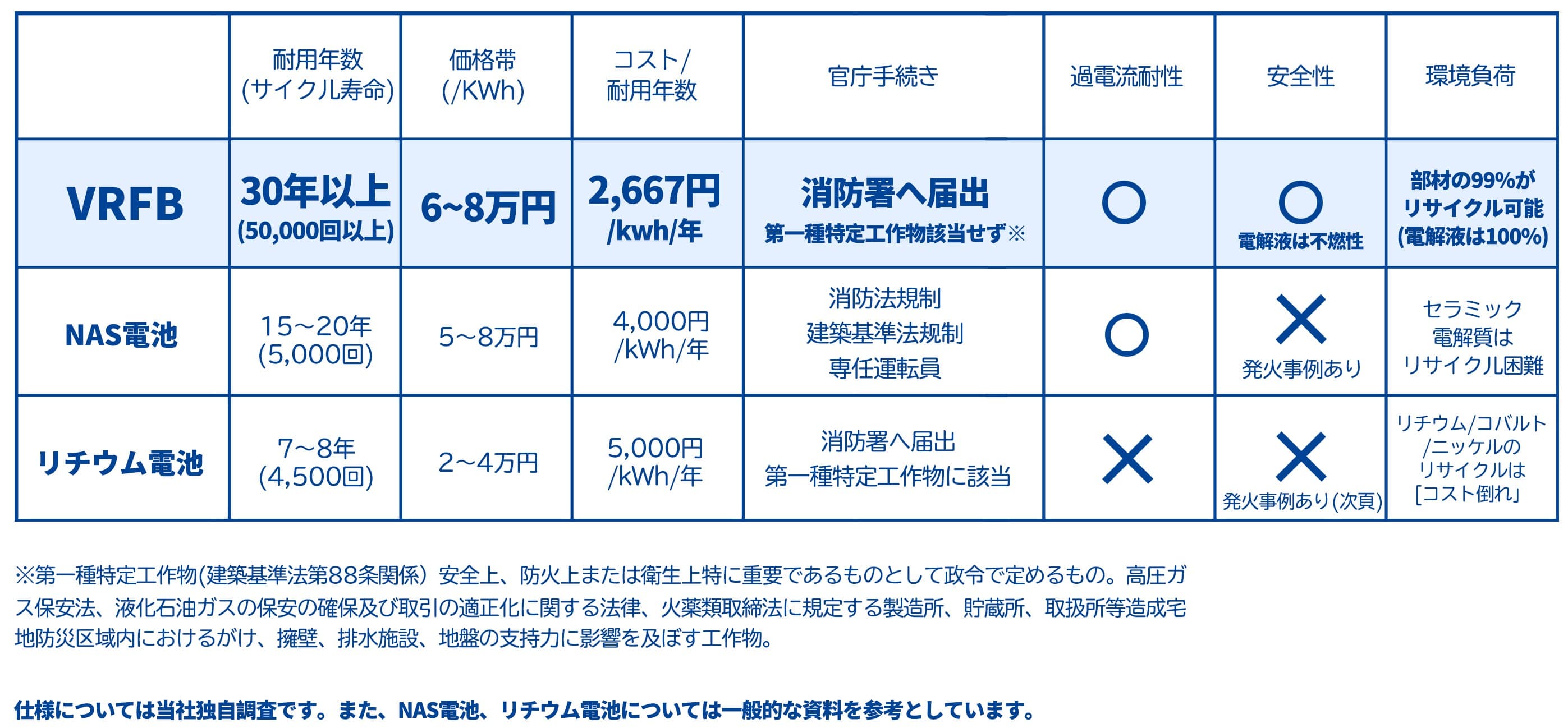
As heat resistance is not required, the battery itself has a long lifespan, with a possible design life of about 20 years. While other batteries have limited charge/discharge cycles, VRFB has unlimited charging/discharging capability, and the electrolyte can be used semi-permanently, enabling cost reduction beyond 20 years.
Scalability Freedom
Storage capacity can be designed by electrolyte volume and output by battery cell stack size individually, enabling free design.
In facilities where public safety is the top priority and social infrastructure requiring long-term stable operation, battery selection is extremely important. VRFB has clear advantages over other major battery technologies, particularly in terms of safety and longevity.
We, LE System, are the only manufacturer in Japan that produces electrolyte, the heart of this excellent VRFB. By stably supplying the highest quality electrolyte domestically, we deliver the highest level of safety and peace of mind to our customers.
3. Diverse Application Scenarios of Vanadium Redox Flow Battery (VRFB)
Vanadium Redox Flow Battery / VRFB Applications
With its high safety and design flexibility, VRFB can meet society's diverse energy needs. As a trump card to resolve power system instability accompanying renewable energy adoption, and as a tool for corporate BCP (Business Continuity Planning) measures and energy cost reduction, its application scope continues to expand.
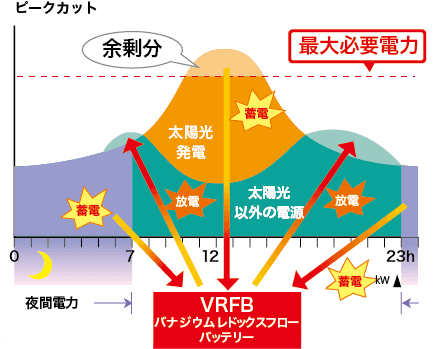
Store surplus solar power during the day or cheaper nighttime electricity, and discharge when solar power is unavailable or during peak demand periods.
Main Use Cases:
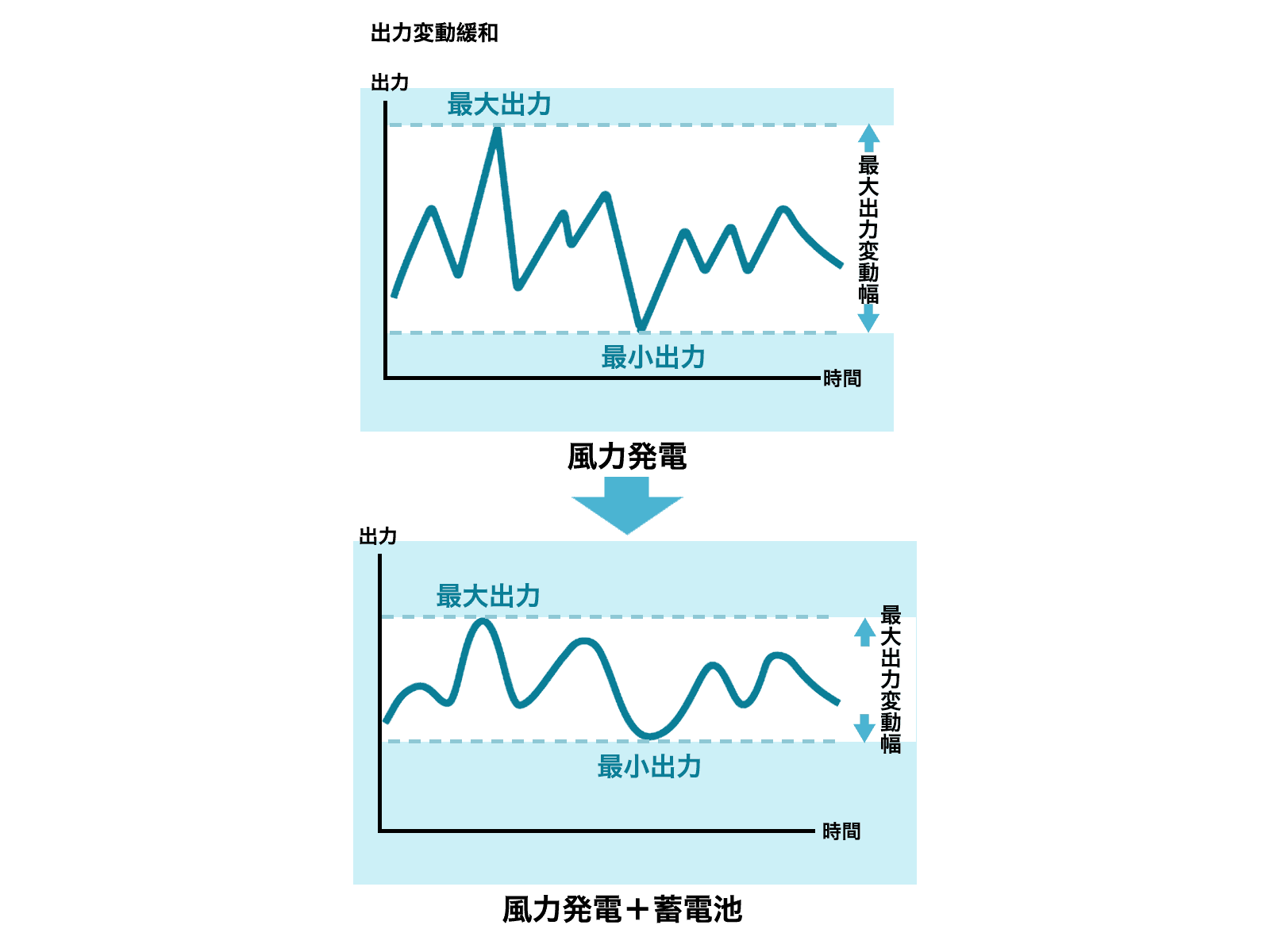
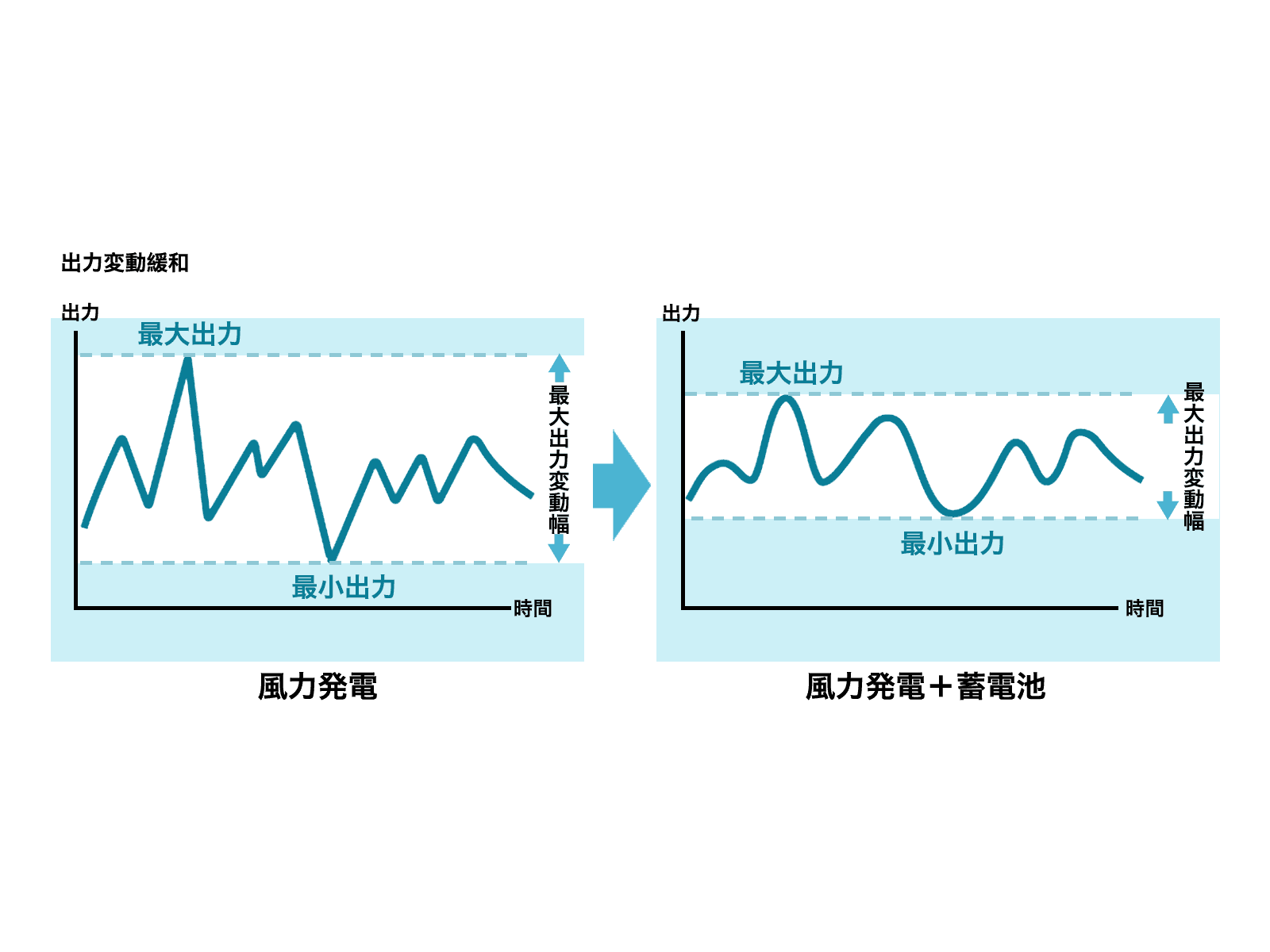
Output Fluctuation Mitigation & Smoothing
Stabilizes renewable energy sources like solar and wind power that fluctuate with weather conditions, maintaining power quality.
Peak Cut & Peak Shift
Charges during low-demand nighttime and discharges during high-demand daytime, reducing basic electricity charges and grid load.
Emergency Power Supply (BCP Measures)
Continues to supply power to critical facilities during outages caused by disasters, protecting businesses and people's lives.
Smart Grid Construction
Serves as distributed power sources that optimally control regional energy, forming the core of next-generation energy infrastructure.
VRFB can flexibly customize capacity and output according to customer needs, from small-scale facilities to large-scale grid applications, providing optimal solutions to all energy challenges.
4. Small and Medium-Sized VRFB Solutions
At LE System, we are advancing the development of small and medium-sized VRFB not only for large-scale grid storage but also for use in more familiar facilities. We are currently promoting the commercialization of "5kW × 4 hours" specification products as 20kWh class batteries that are becoming mainstream, aiming for domestic introduction in Japan.
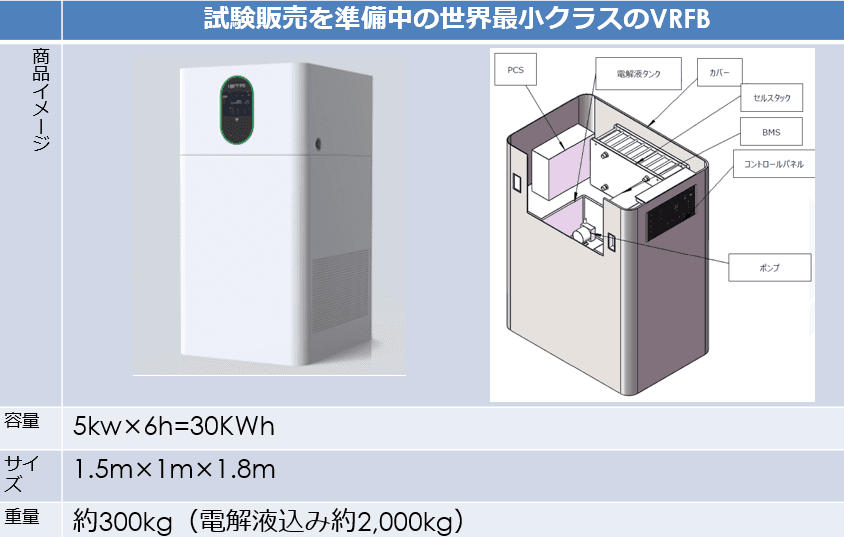
This small and medium-sized model is expected to meet demand especially in places where lithium-ion battery installation is difficult due to fire prevention regulations, and in hospitals, government offices, and elevated facilities that require higher safety. As Japan's only electrolyte manufacturer, LE System is committed to product development so that more people can use high-quality VRFB.
5. About Vanadium Redox Flow Battery Electrolyte
VRFB / Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
High-Quality Electrolyte Supply
vrfb.electrolyte.highQuality.description



Electrolyte specifications can be adjusted according to your requirements. Please contact us for details.
For more information about electrolyte testing and evaluation, please see "Evaluation Technology."
Evaluation Technology